There’s a famous quote from Hippocrates, the father of medicine: “Let food be thy medicine and medicine be thy food.” As we explore the profound connection between nutrition and mental health for women, it’s clear that these wise words ring true. This blog aims to unravel this intricate relationship, offering insight into how a balanced diet contributes to emotional well-being.
The bond between what you eat and how you feel is no secret. It’s an understanding that transcends age, culture, and geography. However, the extent of this connection, especially concerning women’s mental health, has only recently begun to unfold through scientific studies.
So why is nutrition so crucial for mental health? The answer lies in the complex workings of our brains. Our brains require a steady supply of essential nutrients to function correctly and maintain optimal mental health. A lack of these nutrients can disrupt brain chemistry and precipitate mood disorders such as depression and anxiety.
The Power of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, while well-known for their heart-health benefits, are crucial brain boosters. They comprise a significant portion of our brain’s structure and are vital in signal pathways. When our diet lacks these essential fats, our brain function and, consequently, our mental health can suffer.
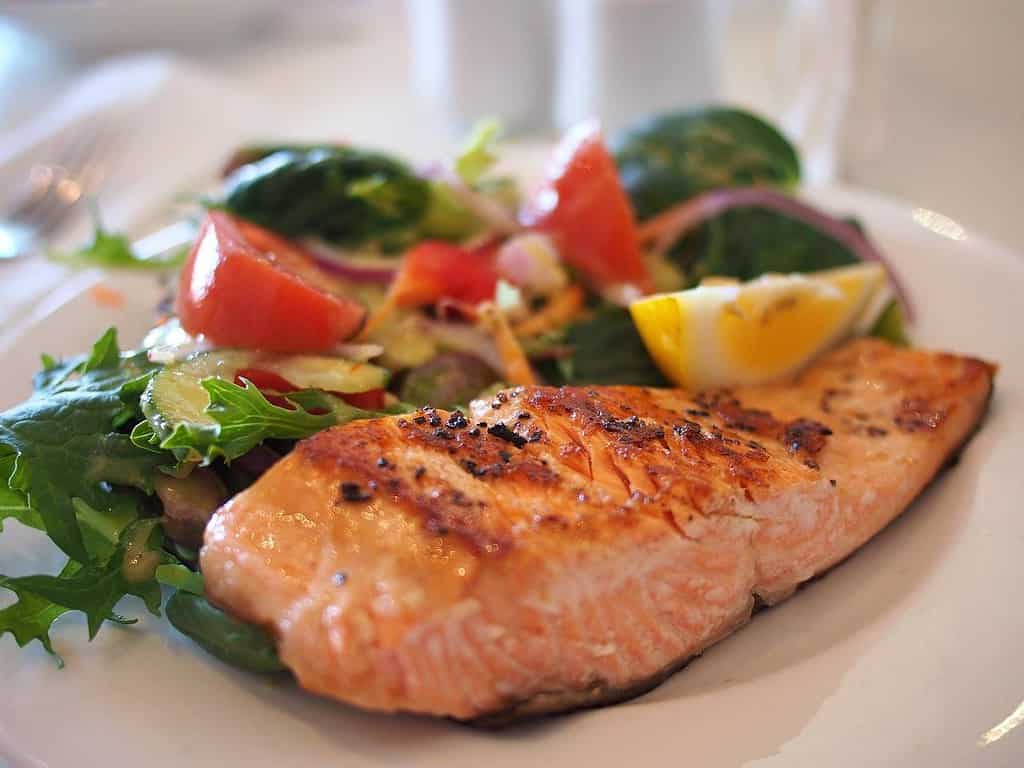
One of the most important types of omega-3 is DHA (Docosahexaenoic acid), which is crucial for maintaining brain plasticity and promoting neurogenesis, the formation of new neurons in the brain. Several studies, including a meta-analysis published in Translational Psychiatry, have shown that omega-3s can help reduce symptoms of depression, underlining their importance in mental health. Foods rich in these healthy fats include fatty fish like salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds.
Complex Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates often get a bad rap thanks to their association with weight gain. However, not all carbs are created equal. Complex carbohydrates in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are integral to our mental health.
These carbs are digested slowly, providing a steady release of energy and helping to regulate blood sugar levels. The result? A balanced mood and improved concentration. Furthermore, they boost the production of serotonin, the “feel-good” neurotransmitter, improving our overall mood and emotional health.
Moreover, a study published in the Nutrition Reviews reported that women who ate more whole grains were less likely to experience depression, showcasing the power of complex carbs.
The Role of B Vitamins
B vitamins are often called “anti-stress vitamins” for a good reason. They play a significant role in our brain’s health, affecting our mood and energy levels. B vitamins (B6, B9, and B12, in particular) produce neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and GABA, which regulate mood and anxiety.
A deficiency in these vitamins can lead to various mental health problems, including depression and anxiety. Therefore, incorporating B vitamin-rich foods like leafy greens, whole grains, and lean proteins into your diet can positively affect your mental well-being.
A systematic review and meta-analysis published in Nutrients found that high doses of B vitamins significantly reduced symptoms of depression. Consider foods like leafy greens, whole grains, and lean proteins to incorporate these essential vitamins into your diet.
Vitamin D: The “Sunshine” Vitamin
Nicknamed the “sunshine vitamin” because our bodies produce it in response to sun exposure, Vitamin D is vital to brain health. It involves numerous brain processes, including neurodevelopment, neuroprotection, and neurotransmission.
Research indicates a strong correlation between low levels of Vitamin D and mental health disorders, including depression. Incorporating Vitamin D-rich foods into your diet and also getting adequate sunshine can contribute to maintaining a good mood and a balanced mental state.
Nevertheless, Vitamin D from sun exposure is vital to brain health. It’s involved in various brain processes, including neurodevelopment and neuroprotection. Several studies, including one published in the Journal of Affective Disorders, found a strong correlation between low Vitamin D levels and depression. Getting enough Vitamin D through diet, sun exposure, or supplements could help maintain a balanced mental state.

Probiotics: Good for the Gut, Good for the Brain
The gut-brain axis, a communication network linking our gut with our brain, plays a vital role in our mental health. Probiotics, often called “good bacteria,” can influence our gut microbiota balance, affecting our mood and mental health. A review published in Annals of General Psychiatry found that probiotic supplements could significantly reduce symptoms of depression, anxiety, and stress.
Probiotics are live bacteria and yeasts that benefit our health, particularly our digestive system. Consuming these friendly microbes can help rebalance our gut microbiota, which in turn, supports our mental health.
Different Types of Probiotics
While the term “probiotics” is used broadly, it encompasses a variety of microorganisms, each with different properties. Two main families of bacteria, Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, make up the majority of probiotics. Here’s a closer look at some of these key players:
- Lactobacillus is the most common probiotic in yogurt and other fermented foods. Different strains can help with diarrhea and as well as people who can’t digest lactose, the sugar in milk.
- Bifidobacterium is found in some dairy products like cheese. They can ease the symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and other conditions.
- Saccharomyces boulardii is a yeast found in probiotics. It appears to help fight diarrhea as well as other digestive problems.
- Streptococcus thermophilus strain promotes healthy digestion and may decrease the incidence of lactose intolerance.
Each of these probiotic strains contributes to a healthy gut in different ways. Thus, consuming a wide range of probiotics can lead to diverse and beneficial gut flora, supporting physical and mental health.
Clinical Evidence of Probiotics and Mental Health
Several studies point to the mental health benefits of probiotics. For instance, a review published in the Annals of General Psychiatry found that probiotic supplements could significantly reduce symptoms of depression, anxiety, and stress. In another study in the Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility, participants who consumed a probiotic-rich yogurt daily showed improved brain function.
Probiotics can be incorporated into our diet through fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha. Probiotic supplements are another way to ensure you’re getting a variety of these beneficial bacteria.
The Nutrient-Mental Health Connection in Practice
Consider the story of Laura, a 35-year-old woman who, after years of struggling with anxiety and mood swings, decided to overhaul her diet. She swapped processed foods for a diet rich in lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats. After a few months, she noticed a significant improvement in her mood and energy levels. Her story echoes the experiences of many others and underscores the role proper nutrition can play in improving mental health.

Nourishing Mind and Body
Understanding the profound connection between what we eat and how we feel opens new avenues for enhancing mental health. From omega-3 fatty acids and complex carbohydrates to B vitamins, Vitamin D, and probiotics, a well-rounded diet can be a cornerstone of emotional well-being. Incorporating these vital nutrients into your diet while practicing other healthy habits like regular exercise, adequate sleep, and seeking professional mental health support can help promote overall mental wellness.
We take a significant step towards nourishing our bodies and minds by embracing a healthier diet. After all, every bit of progress counts in pursuing mental health.
The interplay between nutrition and mental health is profound. A balanced diet, rich in essential nutrients, is crucial in maintaining our brain’s health and promoting emotional well-being. As we continue to learn about this complex relationship, it becomes increasingly clear that good nutrition is invaluable in promoting and maintaining mental health.
Let’s embrace the wisdom of Hippocrates and see our food as our medicine, nourishing our bodies and minds. Here’s to a healthier, happier you!